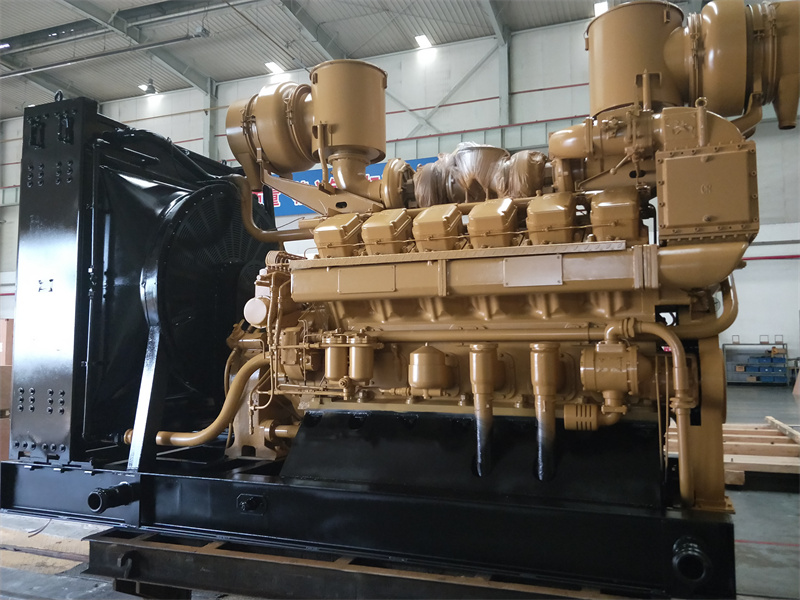
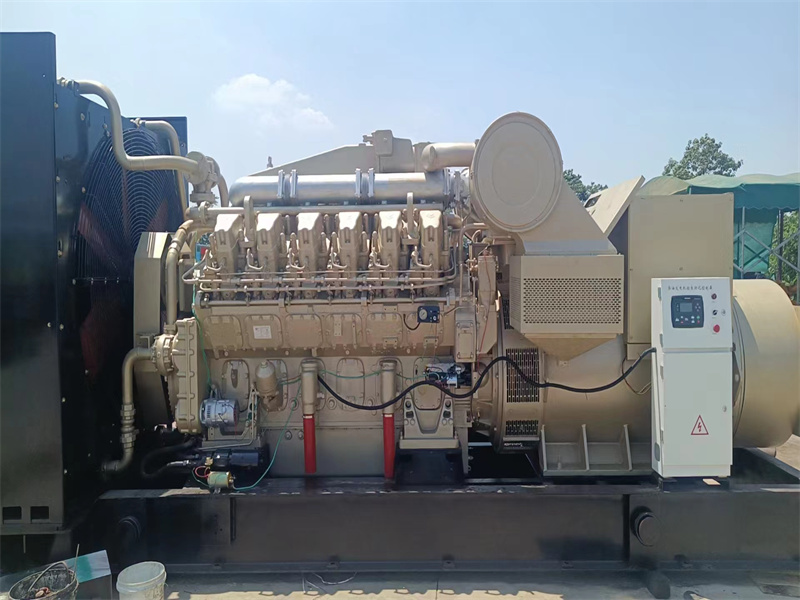
Welcome to Shandong Hongfan Power Technology Co.,Ltd
Technical Data Reference for WEICHAI R6160 Diesel Engines
I. Introduction
The R6160 series diesel engines are four-stroke, in-line, water-cooled, 6-cylinder medium-speed engines. Depending on the air intake method, they can be turbocharged or turbocharged with intercooling. They are available with pneumatic starters or electric starters. Cooling is achieved through a closed-loop cooling system.
II. Technical Data of R6160 Main Engine
| No. | Name | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Engine Type | Inline, four-stroke, direct water cooling, turbocharged. |
| 2 | Number of Cylinders | 6 cylinders |
| 3 | Cylinder Bore x Stroke (mm) | 160 x 225 |
| 4 | Rated Power (kW/rpm) | 164/1000, 184/1000, 220/1000, 276/1000, 328/1000 |
| 5 | Overload Power (kW/rpm) | 180.4/1032, 202.4/1032, 222.2/1032, 303.6/1000, 360.8/1000 |
| 6 | Compression Ratio/Total Displacement (L) | 14.5:1 / 27.14 |
| 7 | Fuel Injection Advance Angle (°A) | 24 ± 1 |
| 8 | Air Intake Method | Turbocharged/Turbocharged with intercooling |
| 9 | Firing Order | 1-4-2-6-3-5 or 1-5-3-6-2-4 depending on the model |
| 10 | Cold Valve Clearance (mm) | 0.35 ± 0.06 |
| 11 | Valve Timing (Crankshaft Angles) | Intake valve opens: 57° BTDC ± 5°; closes: 40° ABDC ± 5° Exhaust valve opens: 46° BBDC ± 5°; closes: 48° ATDC ± 5° |
| 12 | Fuel Consumption Rate (g/kWh) | ≤213/≤210 |
| 13 | Fuel Injector Spray Pressure (MPa) | 19.6/25.4 |
| 14 | Oil Consumption Rate (g/kWh) | ≤1.77 |
| 15 | Oil Pressure (MPa) | 0.2–0.5 (Alarm triggers at ≤0.176) |
| 16 | Water Outlet Temperature (°C) | ≤85 (Alarm triggers at ≥88 ± 3) |
| 17 | Crankshaft Rotation Direction (Viewed from Flywheel) | Clockwise or counterclockwise depending on the model. |
III. Injector and Injection Pump
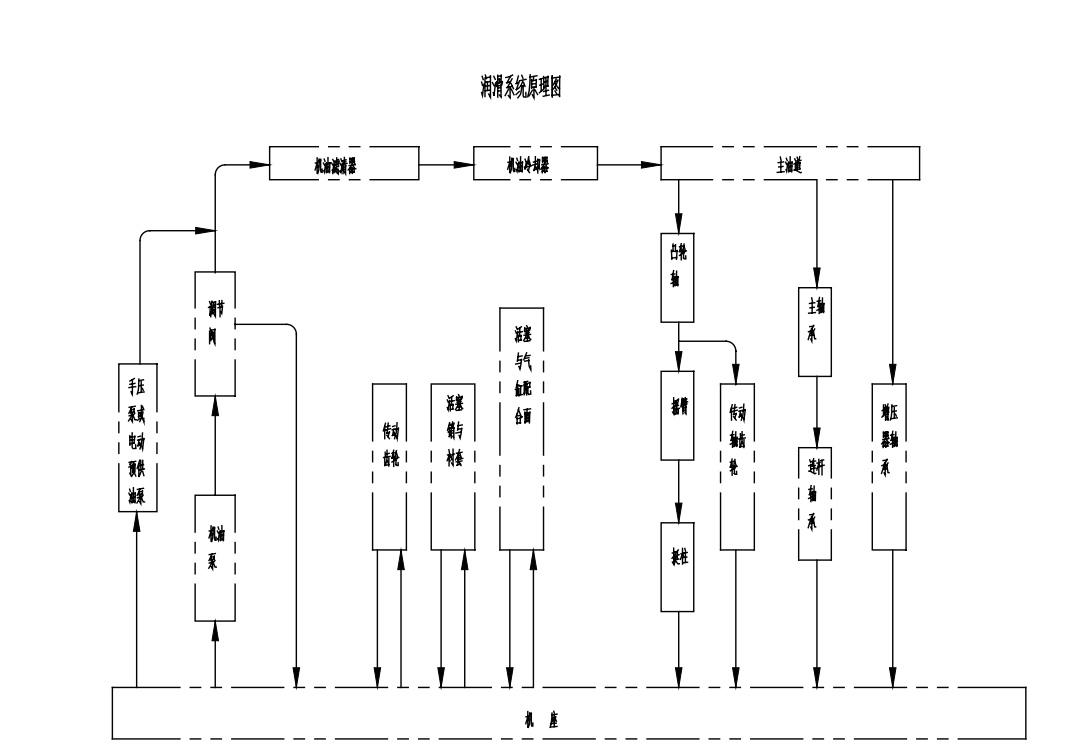
The injector and injection pump are the core components of diesel engine. Improper use, maintenance, or fuel contamination can cause overheating, deformation, or sticking of the injector needle, leading to increased fuel consumption, reduced power output, high exhaust temperatures, and excessive smoke.
IV. Valve Adjustment Based on Firing Order
A. For a firing order of 1-5-3-6-2-4
At TDC of the first cylinder (expansion stroke):
Adjust intake and exhaust valves for the first cylinder, intake for the second cylinder, exhaust for the third cylinder, intake for the fourth cylinder, and exhaust for the fifth cylinder.After 360° rotation (TDC of the sixth cylinder):
Adjust exhaust for the 2ec cylinder, intake for the 3rd cylinder, exhaust for the 4th cylinder, intake for the 5th cylinder, and intake and exhaust for the 6th cylinder.
B. For a firing order of 1-4-2-6-3-5
At TDC of the first cylinder (expansion stroke):
Adjust intake and exhaust valves for the first cylinder, exhaust for the second cylinder, intake for the third cylinder, exhaust for the fourth cylinder, and intake for the fifth cylinder.After 360° rotation (TDC of the sixth cylinder):
Adjust intake for the second cylinder, exhaust for the third cylinder, intake for the fourth cylinder, exhaust for the fifth cylinder, and intake and exhaust for the sixth cylinder.
V. Adjustment of Fuel Injection Timing
Typically, the fuel injection timing is factory set and requires no adjustment. However, if performance issues arise, timing can be checked and adjusted as follows:
Remove the high-pressure fuel pipe of the first cylinder and connect a test tube to the valve seat.
Set the governor lever to maximum fuel delivery.
Manually rotate the flywheel until fuel starts to appear in the test tube, then stop immediately.
The timing pointer on the rear cover will indicate the beginning of fuel delivery for the cylinder.
Reverse procedure applies for engines with opposite rotation.
VI. Common Issues and Solution
A. Engine Fails to Start
Causes: Weak battery, improper control lever position, high oil viscosity, fuel system airlock, water in fuel, improper fuel selection, etc.
Solutions: Check battery charge, adjust control lever, release load, purge fuel system, drain water, or select proper fuel.
B. Insufficient Power
Causes: Incorrect speed, high altitude or temperature, fuel injector issues, clogged filters, improper timing, etc.
Solutions: Adjust speed, clean components, inspect and repair fuel system.
C. Exhaust Smoke
Causes:
White smoke (cold engine, water leakage)
Gray smoke (overload, improper fuel injection)
Blue smoke (oil entering combustion chamber)
Solutions: Adjust load, repair injector, replace piston rings as needed.
D. Abnormal Noise or Vibration
Causes: Incorrect timing, worn components, loose bolts, unbalanced machinery.
Solutions: Adjust timing, replace components, secure machinery.
E. Overheating
Causes: Insufficient cooling water, delayed fuel injection, high environment temperature.
Solutions: Replenish water, adjust timing, and lower load.
F. Low Oil Pressure
Causes: Poor oil quality, blockages, worn components.
Solutions: Use recommended oil, clean system, replace worn parts.
G. Unstable Operation
Causes: Malfunctioning governor, air in the fuel system.
Solutions: Inspect governor, purge air from fuel system.
H. Water Pump Troubles
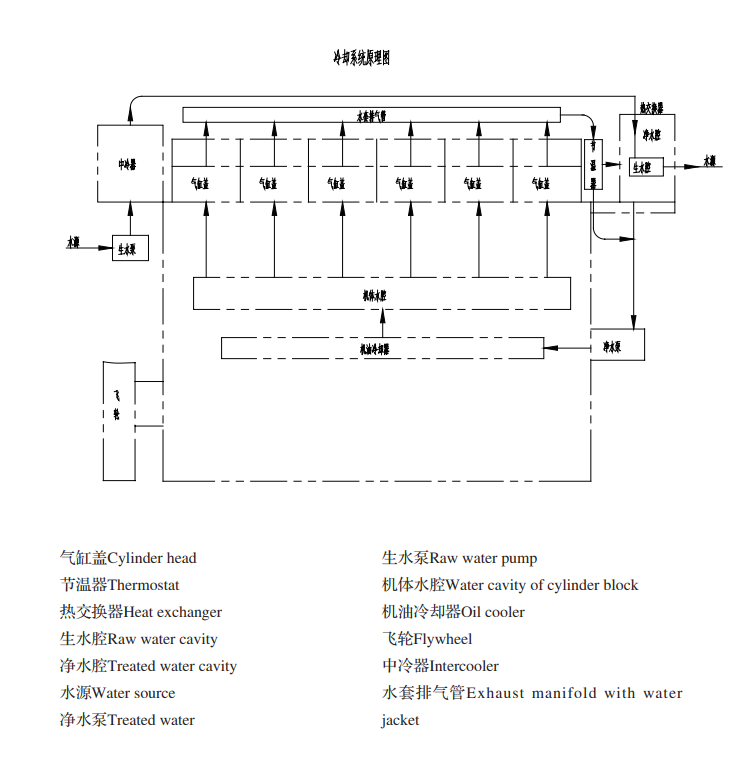
Causes: Airlock, pipe blockage, leaks.
Solutions: Refill water, clean pipes, replace seals.
This detailed guide ensures proper understanding and maintenance of R6160 diesel engines for optimal performance and reliability.










